GitHub Action¶
The PyCharm Security plugin is available as a CI/CD workflow for GitHub Actions on the GitHub Marketplace.
Example¶
This plugin will inspect the GitHub Workplace for Python code and report on vulnerabilities
on: [push]
jobs:
security_checks:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
name: Execute the pycharm-security action
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v1
- name: Run PyCharm Security
uses: tonybaloney/pycharm-security@master
This would give a log of issues inside the report:
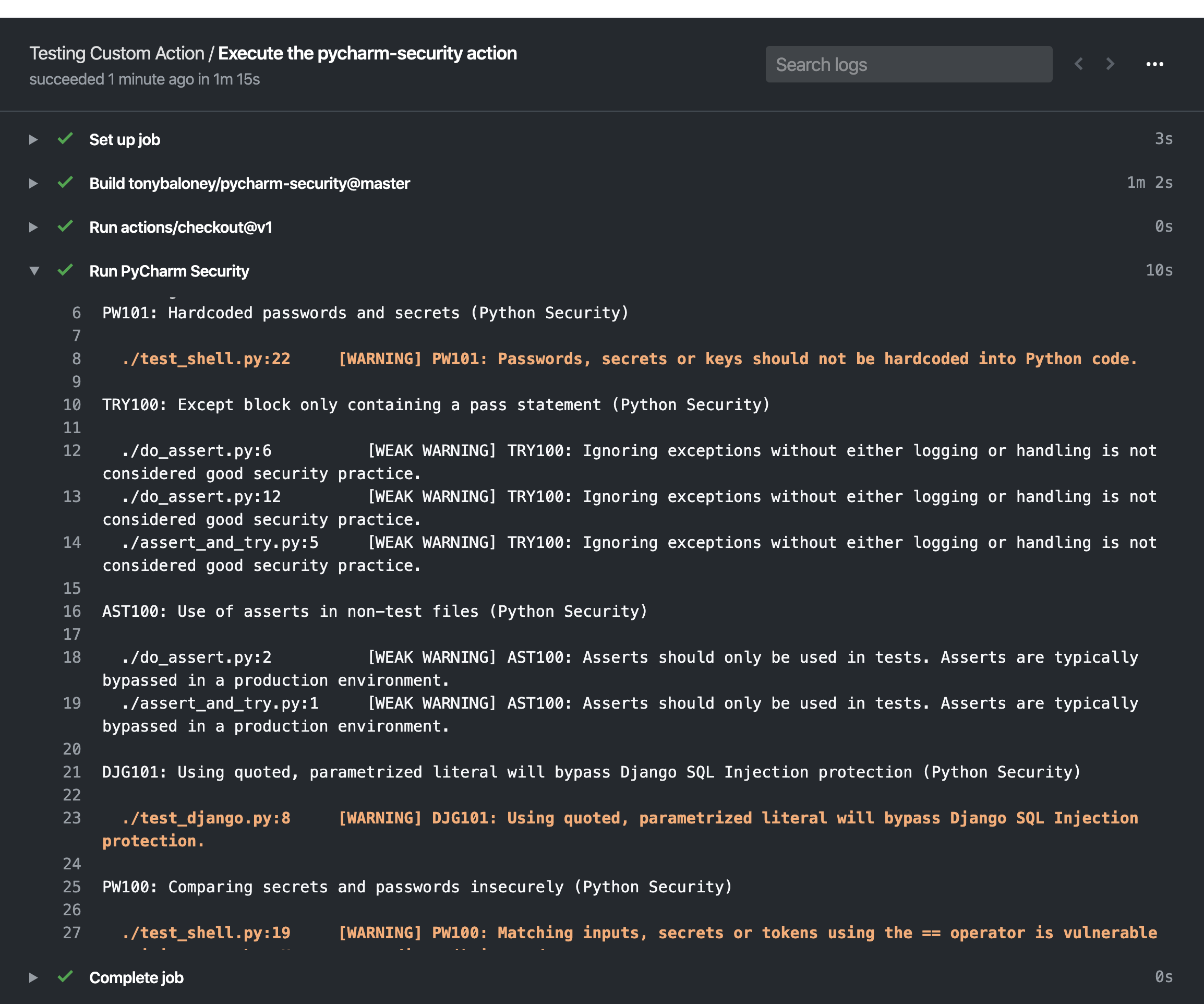
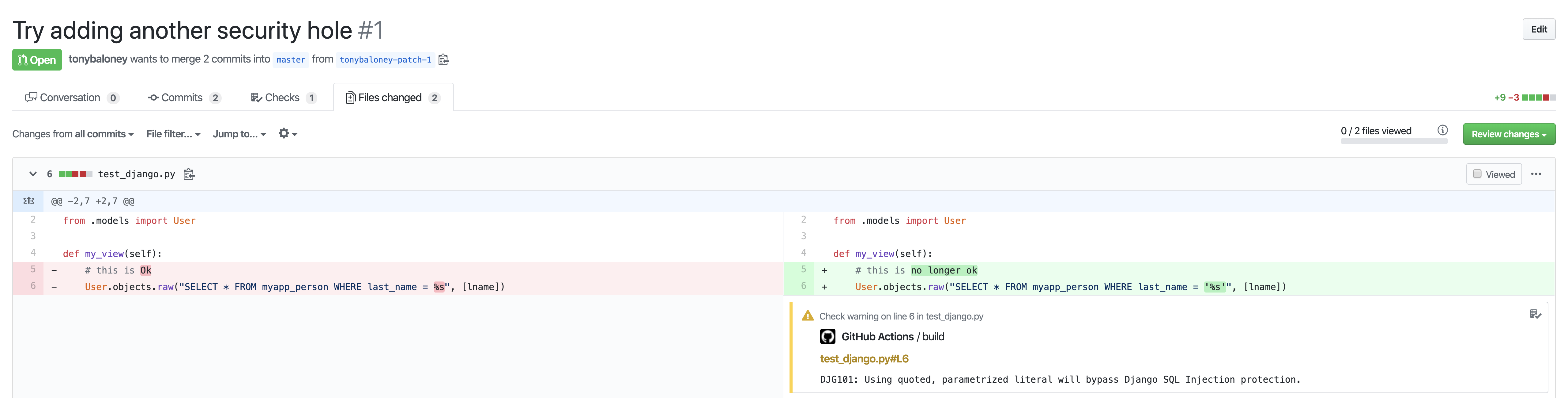
Any issues will be annotated in the files where the changes were detected (such as a commit or pull-request):
List of vulnerabilities and inspections¶
See check index for a list of currently supported inspections.
Additional configuration¶
Specifying target path¶
If you wish to only scan a subdirectory within your code checkout, add the path argument with the relative path from the root.
For example, to scan the src subdirectory:
- name: Run PyCharm Security
uses: tonybaloney/pycharm-security@master
with:
path: src/
Failing a task on warnings¶
If you want the task to fail if warnings were found, use the fail_on_warnings argument and set it to "yes".
Using a custom inspection profile¶
If your project has a custom inspection profile you can use the profile argument and the relative path to your inspection profile XML file.
For example:
- name: Run PyCharm Security
uses: tonybaloney/pycharm-security@master
with:
profile: customProfile.xml
Creating a custom inspection profile from PyCharm¶
Navigate to the Inspect Code from the Code menu
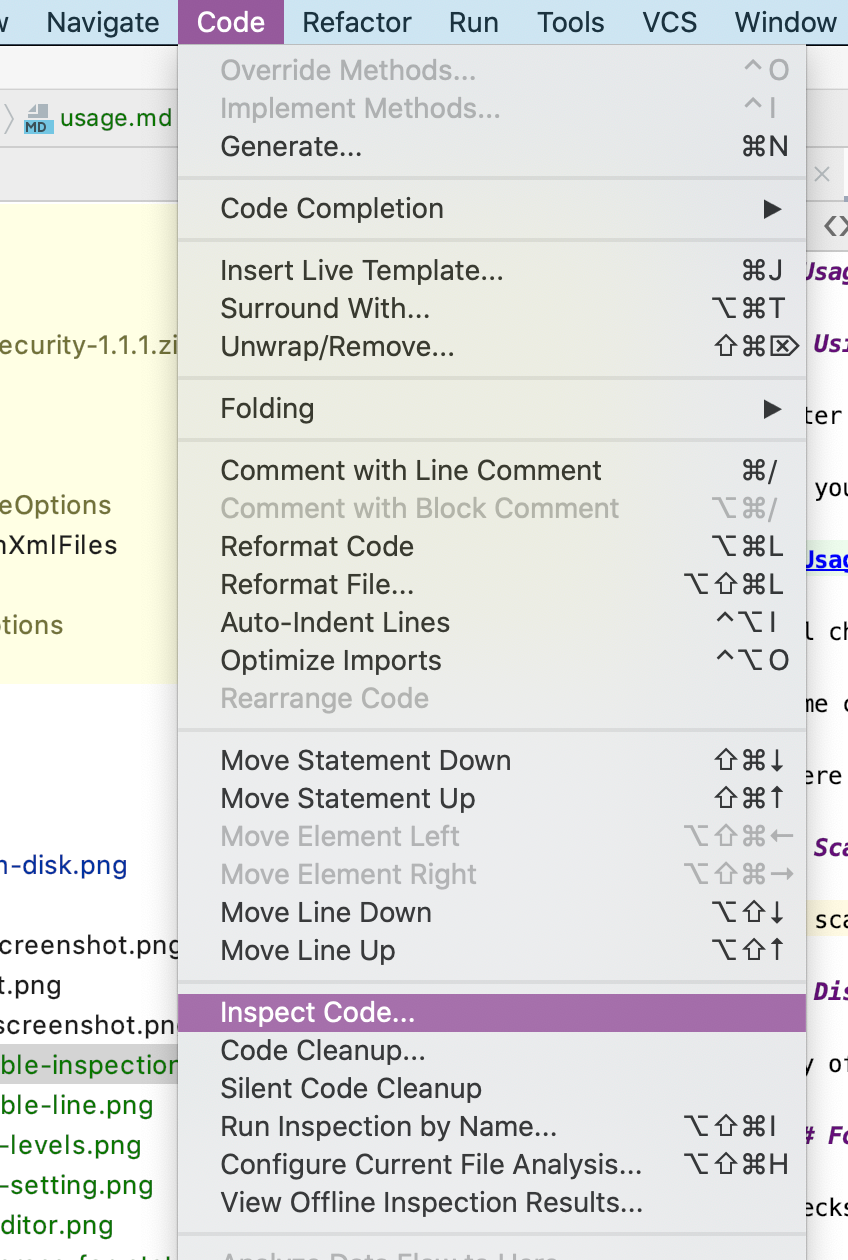
This will pop up with the Inspections Profile Window.
Click the ... ellipsis to edit the inspection profiles.
From here, choose the inspections you want to run, then select the Python Security group:
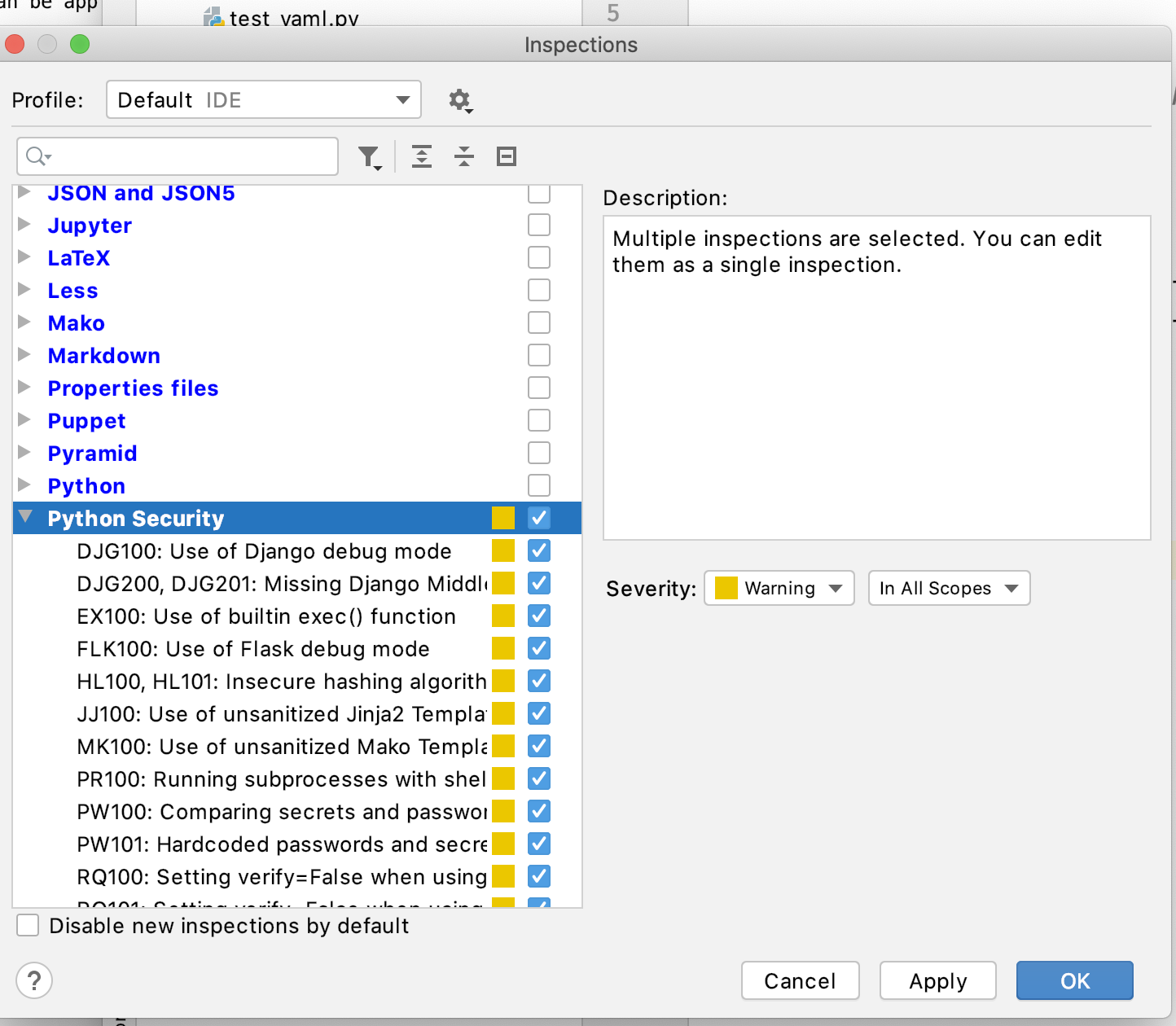
You can customize the severity. Save the inspection profile with the name “Security” (or similar), by clicking on the cog and choosing Copy to Project.
Make sure the inspection profile is checked in to your git repository for the plugin to use it. They are usually saved into .idea/inspectionProfiles/.